|
Shruti Choudhary
Ph.D. Student
LinkedIn, Google scholar
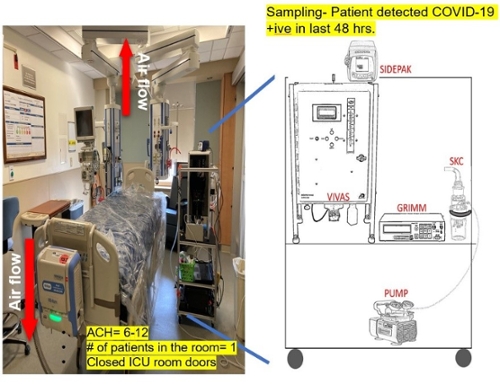
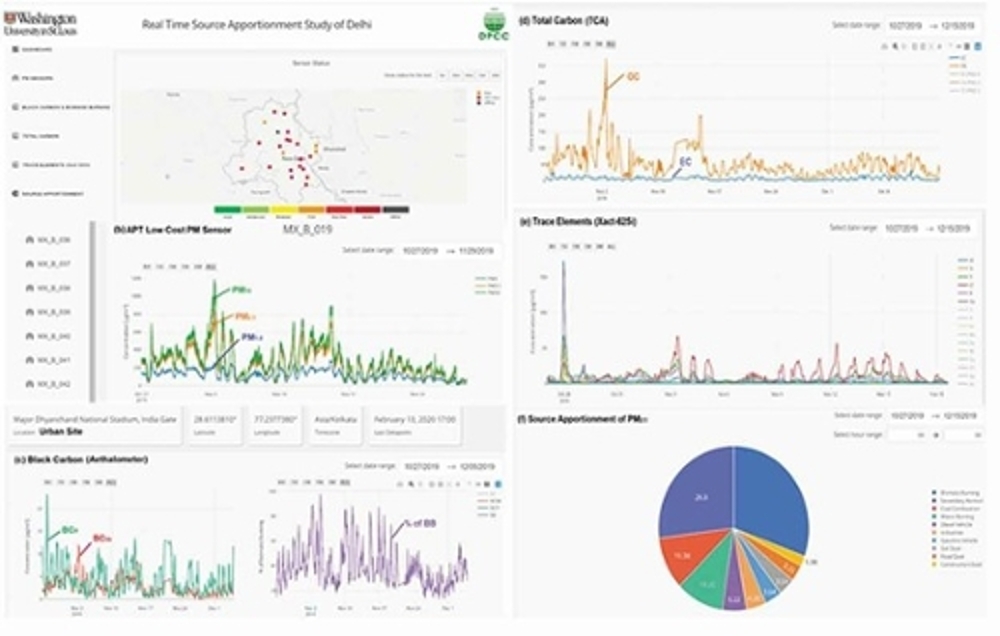
Shruti Choudhary received her B.E. in Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering from Army Institute of Technology (AIT), Pune, India in 2018, where she researched on improving supercapacitors' energy density performance in addition to working at the AIT robotics club for 4 years. After graduating she interned at the Indian Institute of Technology, Indore to work on the synthesis of metal oxide-based material for supercapacitors. She then worked as a consultant at Washington University in St Louis and the Government of Delhi, India for one year where she worked on the Project Real-time pollution source apportionment study of Delhi City. She obtained her master's in Energy, Environmental, and Chemical Engineering from Washington University in St Louis in 2021 and moved to the University of Miami to continue her Ph.D. research work at the Aerosol and Air Quality Research Laboratory. She has worked on many collaborative projects with Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis University Center for Advanced Dental Education, St Louis Children's hospital, St. Louis Symphony Orchestra, The MUNY, and, Applied Particle Technology, Inc.
|